The Comprehensive Guide to Creatine: Benefits, Myths, and Facts
Creatine, widely regarded as a highly effective supplement, remains enveloped in confusion and intrigue despite its extensive use. As one of the most thoroughly researched supplements in the fitness sector, creatine delivers numerous benefits while being surrounded by various myths and misconceptions. Gaining a clear understanding of creatine's role, from enhancing muscle performance to supporting brain function, is crucial in distinguishing fact from fiction.
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, creatine is closely associated with enhanced strength and endurance. The range of its potential benefits is substantial, including boosting muscle mass, enhancing energy production, and possibly offering neuroprotective properties against conditions like Parkinson's. However, alongside these positive attributes, creatine has been at the forefront of discussions regarding its alleged side effects, such as concerns about kidney damage and myths concerning dehydration.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the domain of creatine, assessing its advantages, dispelling common myths, and examining its effects on various groups. Whether you are an athlete aiming to optimize your performance or someone curious about the safety and benefits of creatine supplementation, this article intends to provide clear and evidence-based insights to enhance your understanding.
Understanding Creatine: What It Is and How It Works
Creatine is a naturally occurring amino acid that serves as a key player in energy production within the body. Stored primarily in the skeletal muscles, it combines with phosphate to form creatine phosphate. This compound plays a crucial role in recycling adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in cells, thereby enhancing muscle performance during resistance exercise and other high-intensity activities.
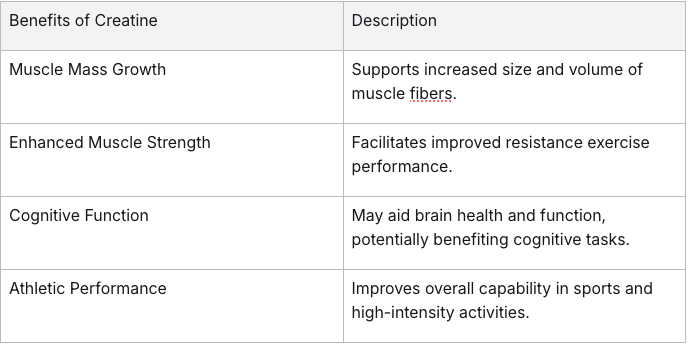
Benefits of Creatine:
Muscle Mass and Strength: Creatine supplementation is widely known to boost muscle growth, strength, and endurance, making it a popular choice among athletes.
Exercise Performance: By enhancing ATP production, creatine improves resistance training outcomes and overall exercise performance.
Cognitive Function: Emerging research suggests that creatine may support brain health and cognitive function, especially during sleep deprivation or intense mental tasks.
Potential Side Effects:
Generally considered safe, creatine consumption can lead to mild side effects such as weight gain due to water retention. However, no substantial evidence links creatine to kidney disease when used responsibly.
Incorporating creatine monohydrate into your dietary supplement regime can support an active lifestyle. Always consult a healthcare professional to tailor dosages according to individual health needs.
Understanding how creatine functions can empower you to make informed choices about its use.
Popularity Among Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
The popularity of creatine among athletes and fitness enthusiasts continues to soar, and for good reasons. As a well-researched dietary supplement, creatine is renowned for its ability to enhance muscle performance and growth. This amino acid plays a crucial role in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), providing the energy necessary for high-intensity resistance training and other athletic activities.
Many athletes pursue creatine supplementation to boost their muscle mass and strength. Creatine monohydrate, the most studied form, is particularly effective in promoting muscle growth and improved body mass through increased muscle cell hydration and enhanced creatine phosphate levels.
Here's a brief overview of creatine's benefits:
While creatine supplementation is generally safe, users should be mindful of potential side effects and consult a healthcare provider if they have conditions like kidney disease.
Creatine's effectiveness for muscle cells and performance enhancement makes it a staple in the regimen of those dedicated to achieving their fitness goals.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation has garnered significant attention in the world of fitness and health due to its multifaceted benefits. As a widely studied dietary supplement, creatine is prized for its ability to bolster muscle mass, boost athletic performance, and enhance cognitive function. Naturally found in foods like meat and fish, creatine is also available in the form of easily accessible supplements. With its role in energy production, creatine helps produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a critical component in energy transfer during high-intensity exercises. Moreover, beyond its muscular benefits, creatine exhibits potential neuroprotective and anticancer properties, contributing to overall wellness. Here is a closer look at the key advantages of creatine supplementation.
Enhancing Muscle Mass and Strength
Creatine is profoundly beneficial for increasing muscle mass and improving strength. As it accumulates in the muscle tissue, creatine enhances water retention within muscle cells, leading to larger muscle size and improved volumization. This increase in cell volume promotes protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. By amplifying creatine phosphate levels, athletes can achieve enhanced power and endurance in resistance training, making creatine supplementation a crucial component for those targeting muscle hypertrophy and overall strength gains. Its ability to support intense training efficiency continues to make creatine a favorite among those focussed on achieving peak physical performance.
Improving Exercise Performance
Prospering exercise performance is a notable merit of creatine supplementation. It is particularly advantageous in activities that require short bursts of high-intensity effort, such as weightlifting, sprinting, and sports that demand quick bursts of energy. By fostering the regeneration of ATP, creatine provides immediate energy to sustain such activities, delaying fatigue and improving workout endurance. Many athletes notice substantial improvements in their physical capabilities, allowing them to train more effectively. As it enhances exercise efficiency, creatine supports improved performance, enabling athletes to push beyond their typical limits and achieve new personal records in their fitness pursuits.
Cognitive Support and Brain Function
Beyond physical enhancement, creatine holds potential benefits for cognitive support and brain function. The brain, like muscles, requires a steady supply of ATP for functioning. By facilitating ATP production, creatine can support cognitive tasks, enhance mental clarity, and improve overall brain health. Research suggests that it may also aid in managing mental fatigue and boosting concentration levels. Furthermore, creatine's role in cognitive support may extend to a protective role in neurological conditions, providing a potential avenue for maintaining mental acuity and cognitive vitality throughout the aging process.
Energy Production in Muscle Cells
Energy production within muscle cells is a cornerstone of physical performance, and creatine plays a pivotal role in this process. Creatine phosphate, stored in muscle tissues, serves as a rapid energy reservoir that can be tapped during intense physical activity. It helps quickly regenerate ATP, providing muscles with the energy needed to sustain high-intensity efforts. This rapid replenishment of energy allows for prolonged periods of exertion, enhancing performance not only in athletic endeavors but also in everyday physical activities. By optimizing energy production, creatine ensures muscles receive consistent and adequate fuel, aiding in recovery and growth.
Neuroprotective Potential for Conditions like Parkinson's
Creatine's neuroprotective potential offers intriguing benefits for individuals with conditions like Parkinson's disease. Research suggests that creatine may help protect neurons from damage, reduce cellular death, and maintain mitochondrial function, which could slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Although more extensive studies are needed, these findings highlight creatine's potential as a supportive supplement for brain health. Its ability to enhance energy stores in brain cells might contribute to maintaining cognitive function and offer a proactive defense mechanism against neurological deterioration, providing hope for those managing such conditions.
Impact on Glucose Management and Heart Health
Creatine supplementation could positively influence glucose management and heart health. By assisting in glucose uptake into muscle cells, creatine may help balance blood sugar levels. This effect is particularly beneficial for those managing insulin sensitivity or striving to maintain stable glucose levels. Additionally, creatine's antioxidant properties may support heart health by reducing oxidative stress and promoting better cardiovascular function. While more research is needed to confirm these benefits conclusively, creatine's potential role in metabolic health adds another dimension to its multifaceted advantages.
Anticancer Properties
Emerging research indicates that creatine may possess anticancer properties, offering promising avenues for cancer prevention and management. It is believed that creatine could inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and impede their energy supply, potentially hindering tumor growth. By supporting cellular energy metabolism and reducing oxidative damage, creatine may provide a supportive role in cancer therapy. While still a developing area of study, these findings suggest that creatine could contribute to a holistic approach to cancer prevention and offer additional benefits beyond physical and cognitive health.
Misconceptions and Myths About Creatine
Creatine supplements are among the most researched ergogenic aids available today, yet a haze of misconceptions continues to surround their usage. Creatine, primarily in the form of creatine monohydrate, is utilized by athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking to enhance muscle mass and improve exercise performance. Despite substantial research affirming its safety and efficacy, several myths persist, causing unnecessary hesitation and misinformation. These misconceptions often stem from misunderstandings about creatine metabolism, its effects on bodily functions, and the various side effects inaccurately attributed to it. Here, we delve into prevalent myths, shedding light on concerns about kidney damage, dehydration, and hair loss, to provide clarity and scientific insights into the true nature of creatine supplementation.
Creatine and Kidney Damage Fears
Concerns regarding creatine and kidney health are one of the most common myths discouraging potential users. The fear largely emanates from the misunderstanding that creatine supplementation can lead to kidney disease or dysfunction. However, research consistently demonstrates that creatine does not adversely affect kidney function in healthy individuals. Studies have shown that while creatine metabolism increases creatinine levels (a waste product filtered by the kidneys), this has not been linked to kidney damage in those without pre-existing kidney conditions. In fact, numerous long-term studies affirm that creatine supplementation is safe for kidney health in healthy populations.
While it's true that individuals with existing kidney disease should approach creatine supplementation with caution, for the vast majority, creatine is safe. The body naturally produces creatine, and supplementation merely elevates these levels to support muscle cells' energy production, especially during high-intensity, resistance training exercises. Consultations with healthcare providers can ensure that supplementation aligns with individual health profiles, eliminating unwarranted fears about creatine and kidney health.
Clarifying Dehydration Concerns
Dehydration concerns are another prevailing myth surrounding creatine supplementation. The theory suggests that because creatine draws water into muscle cells, it may result in overall body fluid imbalance. This misconception implies that creatine users are at greater risk of dehydration, particularly during intense physical activities. However, scientific evidence does not support this claim. In reality, creatine may actually contribute to maintaining hydration by increasing intracellular water retention, which can be beneficial during exercise.
The proper intake of water is crucial, as with any dietary supplements, especially when engaging in resistance exercises or extended physical activity. Users should simply follow standard hydration practices, ensuring they consume adequate fluids alongside creatine supplementation. By doing so, they can enjoy the benefits of enhanced muscle performance and growth without succumbing to dehydration myths. By staying informed and adhering to general hydration guidelines, users can safely incorporate creatine into their fitness routines.
Hair Loss Myths
The belief that creatine contributes to hair loss is another prevalent myth that often deters potential users from considering its benefits. This myth is rooted in the misconception that creatine raises levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair thinning and loss. However, scientific studies have yet to establish a direct connection between creatine supplementation and increased DHT levels. The fear of hair loss remains largely anecdotal, with no concrete evidence to support the claim.
While hair loss can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, stress, and diet, creatine has not been proven to be a contributing factor. Many users safely use creatine supplements to boost muscle growth and athletic performance without experiencing adverse effects on hair health. As misconceptions continue, it’s important to recognize that creatine remains one of the safest, most effective dietary supplements available, providing significant benefits for muscle strength and brain function without impacting hair health negatively.
Safety and Considerations for Different Populations
Creatine supplements are widely used to enhance muscle mass, athletic performance, and brain function. However, the safety and effectiveness of creatine supplementation can vary across different populations. As with any dietary supplement, it's essential to consider individual health factors and lifestyle before starting use. While creatine is generally regarded as safe for most people, specific considerations should be taken into account for distinct groups, such as women and older adults. Understanding how creatine impacts these populations can help maximize its benefits while minimizing any potential side effects. This section explores the unique considerations of creatine use in women and older adults, highlighting factors to consider for safe and effective supplementation.
Creatine Use in Women
While much of the research on creatine has focused on men, growing evidence suggests women can also benefit significantly from creatine supplementation. For women, creatine can aid in enhancing muscle mass and strength, thereby improving overall athletic performance. Moreover, creatine can support muscle growth, making it a valuable addition for resistance training routines. Given the unique hormonal changes women experience, including those related to the menstrual cycle, this supplementation could help maintain muscle fibers and creatine levels more consistently.
Apart from physical benefits, creatine holds potential for improving cognitive function in women, especially since brain health can be affected by hormonal fluctuations. As creatine helps in storing phosphocreatine, crucial for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, it can offer energy support during mental tasks, enhancing both cognitive and exercise performance.
Women considering creatine should weigh the pros of increased muscle performance against any side effects. While creatine supplementation is generally safe, it's wise to monitor individual responses, especially for those with kidney disease or sleep deprivation concerns. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable to tailor creatine use to individual needs and conditions, ensuring safe and effective usage.
Considerations for Older Adults
For older adults, creatine supplementation presents unique benefits and considerations. As the body ages, muscle mass and strength naturally decline, which can lead to decreased muscle performance and increased risk of bone mineral density loss. Creatine can help counteract these effects by enhancing muscle growth and improving muscle strength, thus supporting overall muscle cell health and function in older individuals.
In addition to physical benefits, creatine is noted for its positive impact on brain health. Creatine phosphate, essential for ATP production in muscle and brain tissues, helps in maintaining energy levels, potentially boosting cognitive function among older adults. This can be particularly beneficial in managing age-related cognitive decline, contributing to better brain function and memory retention.
However, older adults must consider potential side effects and tailor creatine supplementation to their specific health context. Those with pre-existing conditions such as kidney disease should approach creatine use with caution. Proper dosage and regular medical consultations can help minimize risks while optimizing the positive impacts of creatine on skeletal muscles and resistance exercise performance. Additionally, focusing on creatine monohydrate, a well-researched form of the supplement, can ensure more predictable outcomes for this demographic. Regular adjustments and professional guidance can aid in integrating creatine safely into an older adult's fitness and health regimen.
Recommended Dosing Strategies for Creatine
Creatine supplementation is a popular approach to enhance muscle mass, strength, and overall exercise performance. To maximize its benefits, understanding the correct dosing strategy is crucial.
Loading Phase: For rapid creatine level increase, a loading phase is recommended. Typically, this involves taking 20 grams of creatine monohydrate per day for 5-7 days, divided into 4 doses of 5 grams each throughout the day. This saturates the muscle cells more quickly, enhancing muscle growth and athletic performance.
Maintenance Phase: After loading, the maintenance phase involves taking 3-5 grams daily. This helps sustain elevated creatine phosphate levels, which supports continuous improvement in resistance training and muscle performance.
Skipping the Loading Phase: Some prefer to skip the loading phase due to potential side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort. In such cases, taking 3-5 grams daily from the start will still be effective, though it may take longer to maximize creatine levels.
Special Considerations: Those with kidney disease or using other dietary supplements should consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance. While creatine is generally safe, monitoring any unusual effects is advisable for optimal results and brain function benefits.
Role of Creatine in Aging Populations
As people age, maintaining muscle mass and strength becomes increasingly important for overall health and quality of life. Creatine supplementation can offer significant benefits for older adults, helping to preserve muscle function and enhance brain health. Creatine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative that plays a crucial role in energy production through the replenishment of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in muscle cells. This energy boost is essential not only for high-intensity exercise but also for everyday activities that help maintain independence in aging populations.
Muscle Preservation and Aging
Aging is often associated with a decline in muscle function and mass, a condition known as sarcopenia. Creatine supplementation has been shown to help counteract this by supporting muscle strength and growth. The presence of creatine phosphate in skeletal muscles enhances muscle fibers' ability to generate energy, which is vital during resistance exercise. This, in turn, aids in maintaining muscle performance and can lead to improved overall body mass in older adults.
Resistance training coupled with creatine supplementation further boosts its muscle-preserving benefits. While resistance exercise alone contributes to muscle growth and increased bone mineral density, the addition of creatine helps in faster recovery and augmented muscle strength gains. In this way, older individuals can not only maintain but potentially increase muscle mass, helping to counteract the natural decline that comes with age.
Beyond physical benefits, there's intriguing evidence that creatine may also support cognitive function in older adults. As the brain’s demand for energy increases with age, creatine can enhance brain health by ensuring a steady supply of energy. By doing so, it may play a role in maintaining mental sharpness, potentially offsetting cognitive decline. Creatine's multifaceted benefits make it a valuable supplement for preserving muscle and brain function in aging populations.
Conclusion: Debunking Myths and Embracing Facts
Creatine is one of the most researched dietary supplements in the fitness community, often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. Many believe it is solely for bodybuilders seeking muscle mass, but evidence shows creatine offers a wide range of benefits beyond muscle growth.
Key Benefits of Creatine:
Muscle Strength and Growth: Creatine supplementation enhances resistance training performance by increasing muscle cell energy, aiding in muscle strength and growth.
Brain Health: It's not just about muscles; creatine supports cognitive function and brain health by contributing to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in brain cells.
Exercise Performance: Creatine phosphate is pivotal for short, intense bouts of exercise, thus improving athletic performance.
Recovery and Performance: Contrary to the myth of serious side effects, creatine supports muscle recovery, even during sleep deprivation.
Clarifying Common Misunderstandings:
Kidney Disease and Safety: Regular doses do not adversely affect kidney function in healthy individuals.
Creatine and Women: It doesn't disrupt the menstrual cycle, offering benefits to skeletal muscles and bone mineral density across genders.
By understanding these facts, you can confidently embrace creatine's benefits for both muscle and brain function.
FAQs
When it comes to creatine, there are several questions that people often ask. Given its role as a popular dietary supplement, it is important to address common concerns to make informed decisions. Whether you're interested in understanding the safety of long-term use, the specific benefits for vegans and vegetarians, or potential side effects, having clear insights can guide your health and fitness journey. Let's explore some of the most frequently asked questions about creatine to provide clarity and debunk prevalent myths.
Is Creatine Safe for Long-Term Use?
The long-term safety of creatine supplements is a topic of interest for many. Research indicates that for healthy individuals, regular, recommended dosages of creatine monohydrate can be safe and well-tolerated over extended periods. There have been concerns regarding potential kidney impairment, but studies have shown that typical doses do not adversely affect kidney function in those without preexisting conditions. As with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a regimen, especially for those with existing health issues. By following guidelines and monitoring health markers, individuals can benefit from creatine’s muscle strength enhancement without significant risk.
Can Vegans and Vegetarians Benefit from Creatine?
Creatine is naturally found in meat and fish, making supplementation particularly beneficial for vegans and vegetarians who may have lower creatine levels due to dietary restrictions. Including creatine in their diet can support muscle performance and cognitive functions, as plant-based diets might lack sufficient levels of this essential compound. Given its role in energy production through ATP, creatine supplementation can enhance exercise performance and muscle mass, aligning well with fitness and health goals. Therefore, vegans and vegetarians stand to gain significantly from creatine, enhancing both muscle and brain function.
What Are the Side Effects of Creatine?
While creatine is considered safe for most people, some may experience minor side effects. Common issues include water retention and gastrointestinal discomfort, but these are generally mild and often mitigated by adjusting the dosage. Creatine does not typically lead to severe side effects when consumed within recommended limits, disproving myths of serious health risks. It’s important to stay hydrated and follow usage guidelines to minimize discomfort. For those with concerns, medical advice can provide personalized insight, ensuring the benefits of creatine use are maximized while keeping side effects in check.